2. Purines versus Pyrimidines:
Purines (2-rings): Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidine s (1-ring): Thymine and Cytosine
3. DNA structure:
DNA is made up of three components: phosphate (have a negative charge, therefore DNA is NEGATIVELY CHARGED), sugar, and the nitrogenous bases. The double helix is also anti-parallel.
4. DNA Replication: The process in which DNA is cloned (Semi-conservative replication). First, Helicase unwinds the helical structure. Primase begins the replication via primers and DNA polymerase III adds nucleotides to form a new DNA strand.
5. Transcription: The process in which RNA is made. First the initiation complex is made from TFs, RNA polymerase II and promoters. RNA polymerase starts transcribing from the template and grabs RNA nucleotide. It stops when the coding strand is at AAUAA (termination sequence).
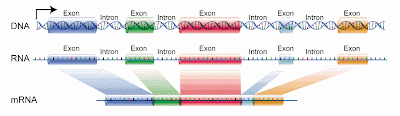
6. Introns versus Exons: Introns are cut out (to become TFs for other DNA strands) and Exons stay in.
7. Ways to protect RNA mutation: Through splicing the introns and the wobble effect of the tRNA (codons).
8. Translation: The process in which pre-mRNA is run through the ribosomes of the ER to form a polypeptide chain.
9. When transcribing DNA follow the following steps:
1. Look for 5' TATA 3'
2. Look for AATAA on the coding strand
3. Look for the intronic sequences
4. Look for 5' ATG 3' on the coding strand
5. Choose which strand is the coding and template and start transcribing (and translating)!
10. Both RNA and DNA grow from 5' to 3' (nucleotides being added to the 3' carboxyl group on the sugar).





No comments:
Post a Comment